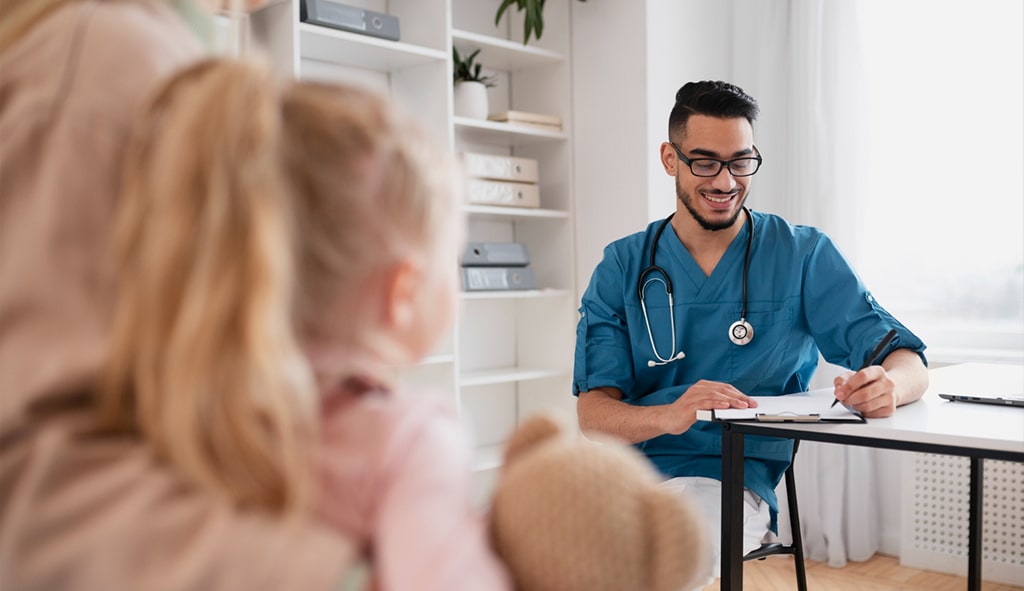
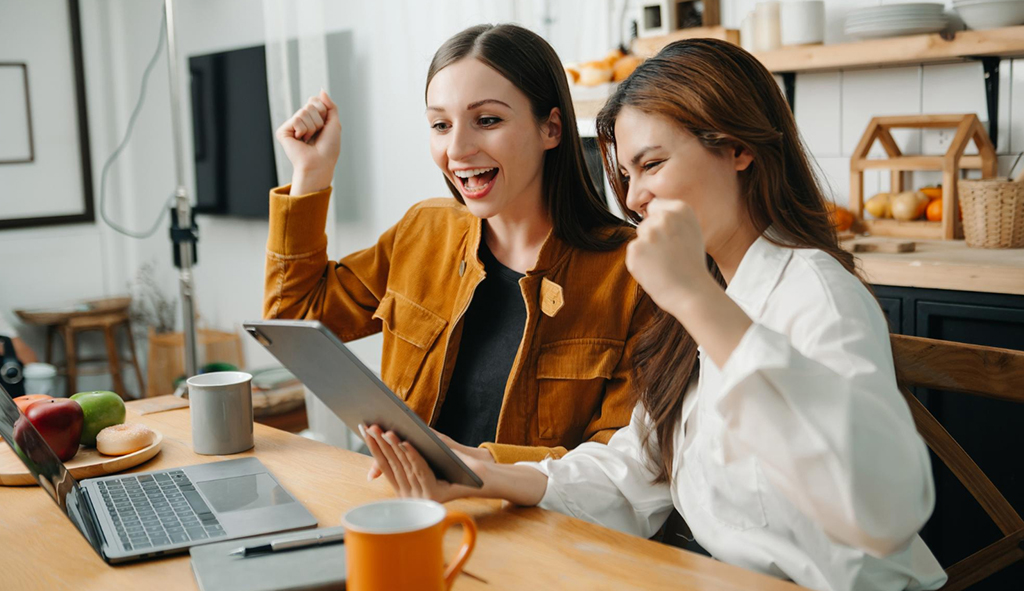
In clinics and hospitals across the United States, a quiet but harmful habit often plays out among family members whose language abilities differ. In particular, when parents don’t speak English fluently, the pressure to bridge the language gap in a medical setting frequently falls on the only bilingual person in the room: their child.
At first glance, the child’s language abilities might appear convenient. After all, who better to help in such a personal situation than a family member who understands both the language and the people involved? A bilingual child might even step in eagerly in these situations, as they may be accustomed to navigating the language barrier at home or in other routine contexts. But in a medical setting, using a skill that seems helpful in the moment can have long-lasting negative consequences for young people.
The Emotional Toll on Children
Being fluent in two languages doesn’t mean a child is prepared to navigate high-stakes conversations, particularly where medical treatment is concerned. But in healthcare settings, many children are asked, implicitly or directly, to relay intimate, complex, and sometimes frightening information between doctors and their parents. This might include explaining a serious diagnosis, parsing detailed treatment options, or conveying medical jargon that the child has never heard before in either language, which can lead to communication inaccuracies.
The emotional burden of translation can therefore be heavy. Children may feel anxious about saying the wrong thing, suffer from guilt if they misunderstand something, or become overwhelmed by the responsibility placed on them. In some cases, they may have to witness their parents in distress, themselves, and feel powerless to help. To put these children’s feelings into greater context, consider that one study demonstrated that trained medical interpreters—that is to say, adults specifically prepared for the role—often experience emotional fatigue, stress, and ethical strain in clinical settings. Imagine, then, the impact on a child trying to perform these duties without professional training, the maturity that comes with age, or any form of external support.
How Providers Can Improve Language Access
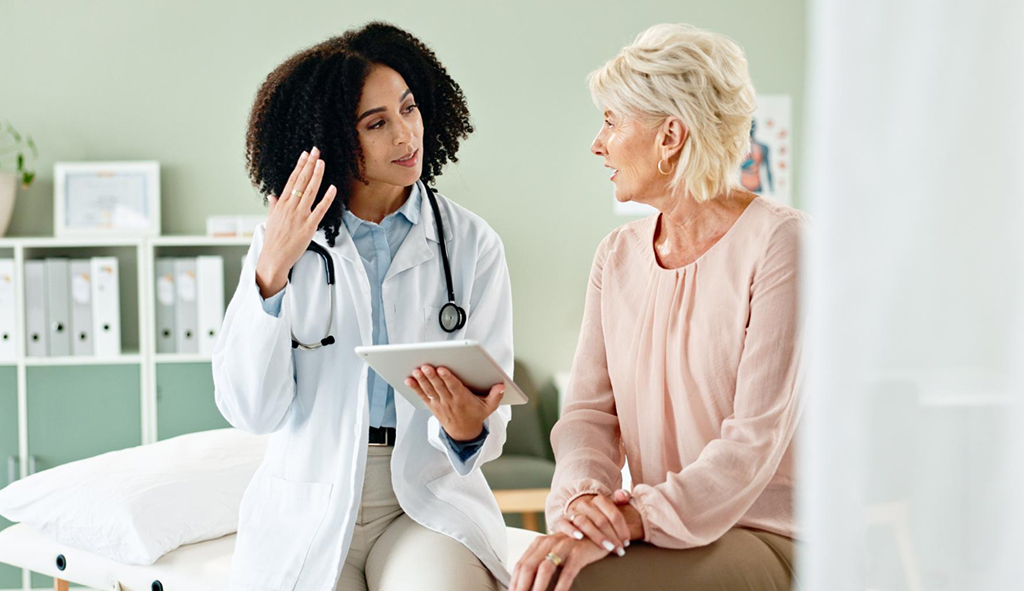
Because there is such risk involved in relying on children to convey critical medical information, it’s clear that providing families with information in their own language should be a priority. Medical communication should not be performed on the fly; it should be proactive, professional, and grounded in care for the patient.
Once hospitals have established and adopted clear language access policies, it becomes easier for staff to know which documents require translation, in what languages, and how to obtain them. Instead of scrambling on a case-by-case basis, teams are equipped from the start with a system that prioritizes access and equity.
Here’s how providers can move away from risky practices toward more inclusive, sustainable solutions:
- Educate frontline staff
It’s easy to assume that everyone understands the potential harms of depending on children to communicate medical information. Unfortunately, however, these risks aren’t always intuitive.. That’s why staff should receive training in the ethics involved with translation so they can understand exactly how to access professional translation support. When that process is simple and streamlined, patients are more likely to receive the right care, at the right time, in the right language. - Use pre-translated templates and integrate them into EHR systems
Many healthcare interactions, like discharge instructions or consent forms, follow standard processes. These documents can be professionally translated in advance and stored as templates, so they’re ready to access when needed. When integrated into the electronic health record (EHR) system, these templates help ensure consistent, accessible communication across departments without delays. - Build trust with LEP families
From the first point of contact, let families know that translated materials and language support are available to them. When they trust they’ll receive information in their own language, there’s no need for their child to step in. This not only protects the child from unnecessary emotional stress, but it also shows respect for the family, acknowledges the dignity of their primary language, and helps build a foundation of trust in their healthcare experience.
Prioritizing Access at Every Step
To move forward in medical translation means making language access a built-in part of care, not an afterthought. When translated materials are ready, institutional policies are clear, and medical teams are trained to respond confidently, everyone benefits. By investing in professional translation, medical facilities can ensure families receive the clarity they need, and the system becomes more equitable, efficient, and compassionate for all.