AI has found its voice—literally. In the world of media localization, AI-powered voiceover and dubbing tools are transforming the way that organizations create multilingual content. These technologies offer a faster, more scalable approach to audio localization, making voiceover capabilities accessible to a wider range of industries and budgets. While this shift is promising, it also demands that localization experts strike an increasingly thoughtful balance between automation and human expertise.
Behind the Scenes: How AI Dubbing Works
At the heart of AI dubbing lies advanced speech synthesis, a technology that turns adapted scripts into lifelike voiceovers. Here’s how it works:
- Input: A script or text file is provided to the AI system. This script has been previously adapted to the required language by a professional media localizer, and it’s properly adjusted to the time constraints of the video.
- Processing: The AI system treats the script or text file with a technology called speech synthesis—also known as text-to-speech or speech-to-speech. This engine has two main components: a front-end and a back-end. The front-end prepares the text by converting symbols, like numbers and abbreviations, into full words. This process is often referred to as text normalization. The front-end also determines how each word should sound (aka text-to-phoneme conversion) and organizes the text into phrases or sentences with appropriate rhythm and intonation (prosody).
- Output: The back-end of the engine, also called the synthesizer, takes this prepared information and converts it to sound: the final speech output. This product can range from a neutral voiceover to region-specific accents, depending on the tool’s capabilities.
The advanced speech synthesis workflow is especially useful for scalable, lower-budget projects like e-learning, product tutorials, corporate training, or even social media content. For creators and companies alike, it brings a powerful opportunity to localize at scale—without the complexity of a traditional studio setup.
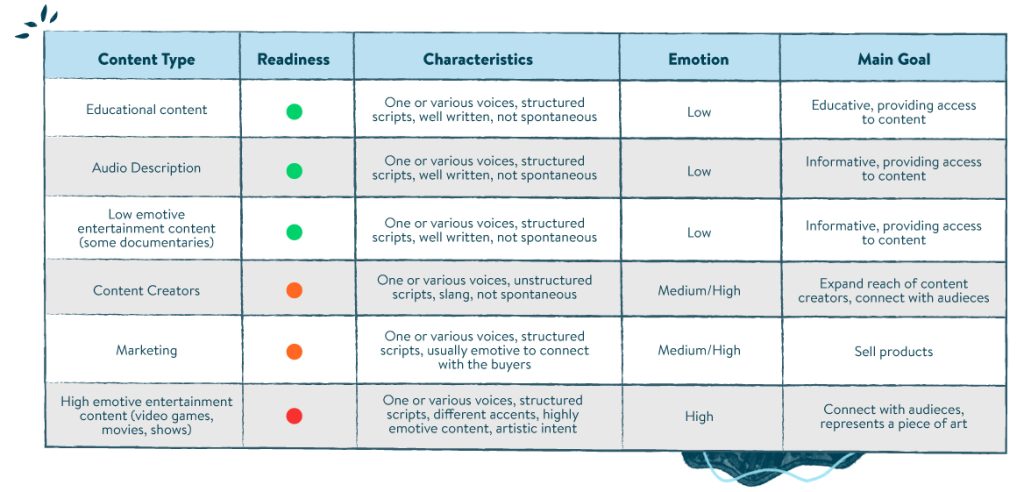
When Is AI Dubbing the Right Fit?
The table below offers a more-detailed breakdown of the ways in which AI dubbing can be a smart choice for certain types of content, particularly where production budgets are limited or speed is crucial. Use cases range from educational content and audio descriptions to lower-emotion entertainment, like documentaries. Content creators and marketers are also turning to AI dubbing to expand their reach—especially with platforms like YouTube integrating autodub features.
But as the table also indicates, there can be limits to AI’s efficacy with content consumers. For emotionally charged productions like films, TV shows, or video games, for example, audiences expect nuance. This is where AI still struggles—and where human-generated post-editing must bridge the gap.
Enter the Scene: The Role of Post-editing
Post-editing plays a pivotal role in refining AI-generated dubbing to ensure it resonates with audiences and meets production standards. Beyond technical edits, post-editing also involves prooflistening—a final review that focuses on the listener’s experience. This step helps detect subtle inconsistencies or audio distractions that may go unnoticed in the editing process.
To deliver high-quality results, post-editors must bear in mind:

- Regional Accents and Voice Consistency, which ensure cultural authenticity and coherence throughout the audio, and are especially important when dubbing for specific markets or across multiple episodes or segments.
- Speech Rate and Pronunciation, which improve clarity and flow by adjusting unnatural pacing or correcting mispronunciations. These are the sort of fixes that help the audience stay effortlessly engaged.
- Emotional Accuracy, which ensures the tone reflects the original performance. Whether the source content was exciting or languid, comical or sincere, the dubbed version must feel genuine and fully aligned with the original material’s intent.
- Lip-Sync Matching. This component of post-editing oversight, which is essential for visual content, ensures that spoken words align with on-screen lip movements. It serves to safeguard audience immersion and maintain professionalism in video formats.
- Client-Specific Audio Specs. These considerations cover everything from volume levels to file formatting. They ensure that the audio is ready for final delivery and integration with other production elements.
Each of these post-editing considerations contributes to a seamless viewer experience—and it’s the human attention to these very human details that sets the final product apart.
Conclusion
AI dubbing is evolving fast, bringing greater access to localized voiceover than ever before. For global organizations and creators with growing content demands, it’s a powerful tool that unlocks speed and scale. But even as the technology improves, human involvement in the dubbing process remains essential. That’s specially true when the goal isn’t just about being understood, but about being truly heard—in the right voice, at the right time, by the right audience.