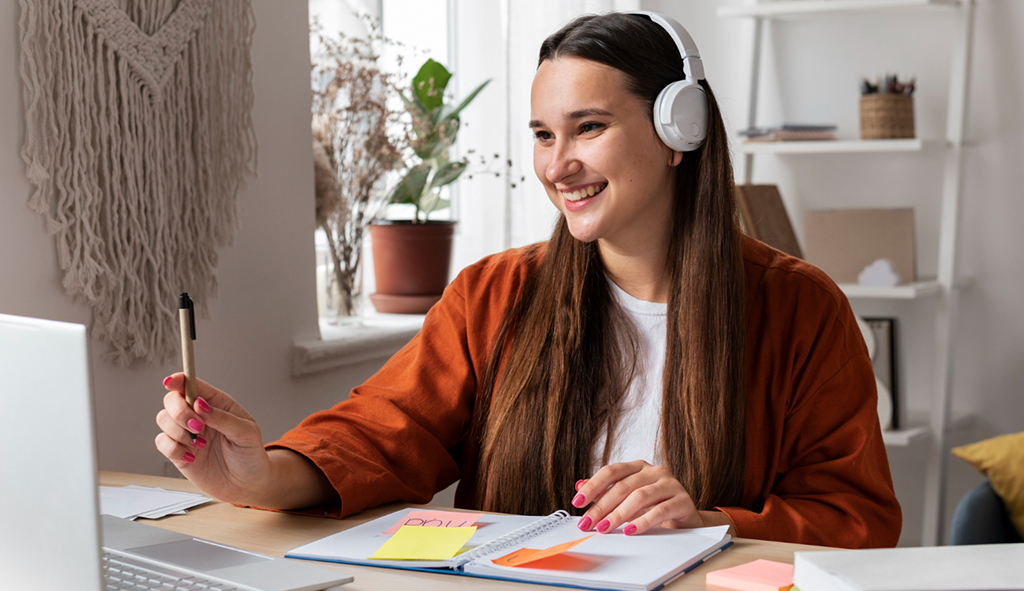
Multilingual communities have always been part of the healthcare landscape in the U.S., but an increase in global migration, cultural diversity, and intergenerational households means that medical providers are interacting with growing numbers of patients who speak languages other than English.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, about 21.7% of people speak a language besides English at home. Spanish leads the list, followed by Chinese and Tagalog. At the same time, data from UnitedHealth Group shows that 36% to 59% of the U.S. population resides in counties with the lowest health literacy levels. Therefore, in places where multilingualism is common, translation services are foundational to equitable healthcare, and there is still much work to be done to ensure these communities have the medical language access they both require and deserve.
The High Stakes of Language Barriers
Health literacy already presents a challenge for many patients in the U.S., with nearly 25% of adults reading at or below a 5th-grade level, while most medical documents require 10th-grade comprehension or higher. That gap grows even wider for patients in the U.S. who hail from multilingual communities, where language and cultural differences can compound existing barriers to understanding.
When critical information is not translated or adapted for these patients, they are left to interpret complex instructions alone. The ramifications of this negligence can be catastrophic. In one widely reported case, a Vietnamese family in the U.S. lost their 9-year-old daughter after she experienced an adverse reaction to a medication she’d been prescribed. Her family had not been issued adequate instructions about at-home care or what to watch for in the event of a bad reaction, and a lack of proper medical interpretation meant the child’s caregivers could not effectively communicate what was happening. The girl’s subsequent death is a tragic example of the essential importance of language access to patient safety.
Why Professional Translation Makes All the Difference
Professional translation services can bridge such communication gaps by ensuring that healthcare information is accessible, accurate, and culturally relevant. For instance, a well-translated discharge summary ensures a patient understands what medications to take, when to schedule follow-ups, and how to monitor for complications.
Specialized medical translators reduce the risk of ambiguity and error by clarifying terminology for patients and caregivers, and their cultural competence also allows them to localize content, meaning that patients understand medical content in a way that is adaptive to their culture’s health beliefs and norms. The difference between a quick translation and a culturally tailored one can determine whether a patient feels seen, or sidelined.
When Patients Understand, Everyone Benefits
When language barriers are removed in a medical situation, the benefits go both ways. Providers, too, gain more clarity on their patient’s situation, they gain more trust from patients and their families, they are able to be more efficient in their treatment, and they’re likelier to achieve better outcomes. Patients who fully understand their care are better equipped to follow treatment plans correctly, which reduces the chance of otherwise-avoidable complications, repeat visits, or emergency interventions.
For healthcare teams, a better understanding also leads to smoother coordination with families, and lower liability risk. Clear communication also supports stronger patient relationships, which is key to today’s value-based care models in which satisfaction and outcomes matter more than ever.
Finally, from a healthcare provider perspective, professional translation ensures compliance with legal and accreditation standards, which helps organizations meet both ethical and regulatory benchmarks.
Conclusion
Language should never be a barrier to safe, quality healthcare. Professional translation, therefore, reduces health risks, builds trust between provider and patient, and ensures that every patient, regardless of the language they speak, can access the information they need to make informed decisions about their health.
When patients understand their care, outcomes improve. And when healthcare providers invest in language access, the entire system becomes safer, more inclusive, and more effective.